To create a thread under Solaris, use function thr_create(). Note that all thread related functions start with thr_. The syntax of thr_create() is:
int thr_create(
NULL, /* use this default */
0, /* use this default */
void *(*funct)(void *), /* thread funct */
void *arg, /* argument passed to funct() */
0, /* use default */
thread_t *ID); /* use NULL works fine */
Calling thr_thread() will create a child thread which will
execute concurrently with the parent thread (i.e., the caller).
The following is the meaning of each argument:
![]()
#include <stdio.h>
#include <thread.h>
void *count(void *JunkPTR)
{
int *valuePTR = (int *) JunkPTR; /* convert to integer ptr. */
int value = *valuePTR; /* then take the value */
printf("Child: value = %d\n", value);
}
void main(void)
{
thread_t ID1, ID2; /* for thread IDs */
int v1 = 1; /* argument for the 1st thr */
int v2 = 2; /* argument for the 2nd thr */
thr_create(NULL, 0, count, (void *) (&v1), 0, &ID1);
thr_create(NULL, 0, count, (void *) (&v2), 0, &ID2);
printf("Parent\n");
sleep(2); /* why is sleep() here? */
}
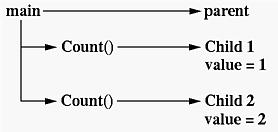
The following diagram shows the three concurrently executing threads, one parent (i.e., the main program) and two children (i.e., the two copies of count()).